Sets
Organize, save, and share your API testing workflows with Quetzly's Sets feature. Sets allow you to create collections of related requests, making it easy to manage complex testing scenarios and share configurations with team members.
What are Sets?
Sets are collections of saved API requests that include:
- Request configurations: URLs, methods, parameters, headers, and body content
- Service types: WMS, WFS, ArcGIS, or standard REST API configurations
- Export/Import capability: Share sets with colleagues or backup your configurations
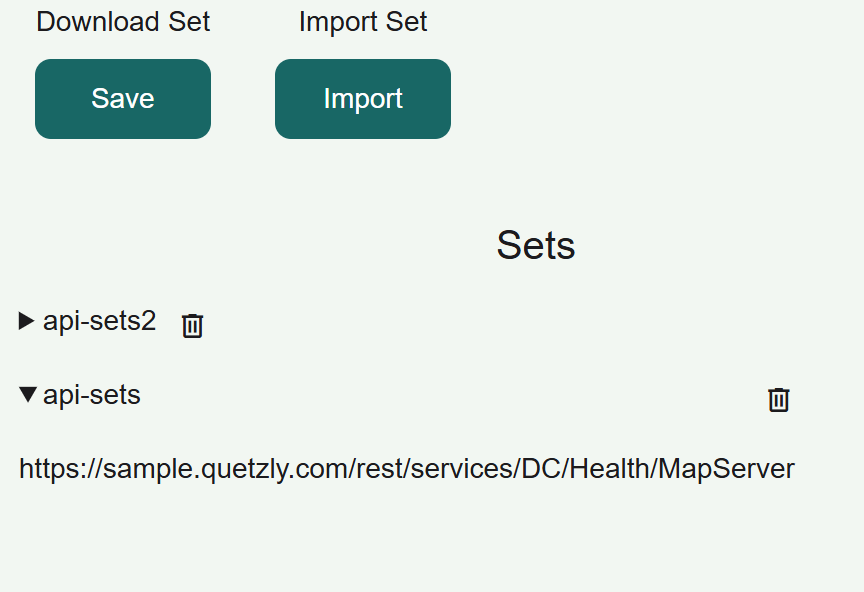
Accessing the Sets Interface
- Click the
Sets icon in the left sidebar
- The Sets panel displays:
- Download Set: Export your current configurations
- Import Set: Load saved configurations
- Sets List: View all your saved request collections
Creating and Managing Sets
Saving Your Current Work
Download Set (Export)
- Configure your requests in the API section
- Navigate to the Sets section
- Click the "Save" button under "Download Set"
- Choose a location to save your
.jsonconfiguration file - Name your file descriptively (e.g.,
company-wms-services.json)
The exported file contains:
- All current request parameters
- Headers and authentication settings
- Service type configurations
- Any custom settings or preferences
Note: The export feature will download a json file of all layers currently on the map.
What Gets Saved
- ✅ Request URLs: All endpoint addresses
- ✅ HTTP methods: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
- ✅ Service types: WMS, WFS, ArcGIS, JSON selections
- ✅ Query parameters: All key-value pairs
- ✅ Headers: Including authentication headers
- ✅ Request bodies: JSON content for POST/PUT requests
Set File Format
For a set to load successfully, it must follow this JSON structure:
{
"layers": [
{
"url": "https://api.example.com/endpoint",
"method": "POST",
"type": "JSON",
"params": {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
},
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer [YOUR-TOKEN]"
},
"data": {
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [-122.4194, 37.7749]
},
"properties": {}
}
}
],
"timestamp": "2025-11-30T12:00:00.000Z"
}
Required fields:
layers(array): Contains all request configurationsurl(string): The API endpoint URLmethod(string): HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE)type(string): Service type (WMS, WFS, JSON, ArcGIS)
Optional fields:
params(object): Query parameters as key-value pairsheaders(object): HTTP headers as key-value pairsdata(object): Request body for POST/PUT requeststimestamp(string): ISO 8601 timestamp of export
Common format errors:
- Missing
layersarray - Invalid JSON syntax (missing commas, brackets, quotes)
- Incorrect data types (string instead of object)
- Malformed URLs or invalid HTTP methods
Loading Saved Sets
Import Set
- Click "Import" button under "Import Set"
- Browse to your saved
.jsonfile - Select the configuration file
- Confirm the import
- The requests will be loaded and available in your Sets list
Import Behavior
- Additive: Imported sets are added to existing sets (no overwrite)
- Validation: Invalid configurations are skipped.
- Restoration: All parameters, headers, and settings are restored
- Immediate availability: Imported sets appear instantly in the Sets list
Managing Your Sets Collection
Sets List Interface
The Sets list shows:
- Set names: Descriptive names for each collection. It's defined by the files name.
- Actions: At the moment there is only delete action but more to come.
Loading a Set
- Locate the desired set in the Sets list
- Click on the set name or "Load" button
- The requests are loaded into the API interface
- Switch to API section to use the loaded requests
- Modify parameters as needed before sending
Practical Use Cases
Development Workflows
API Development Testing
Create sets for:
- Development environment: URLs pointing to dev servers
- Staging environment: Pre-production testing configurations
- Production environment: Live service testing (use carefully)
- Local testing: localhost and development server configurations
Feature Testing Suites
Organize by functionality:
- Authentication tests: Login, token refresh, logout flows
- CRUD operations: Create, read, update, delete sequences
- Spatial queries: Various geometry-based requests
Team Collaboration
Sharing Configurations
Export for colleagues:
- Create comprehensive sets with your working configurations
- Export to shared network locations or version control
- Include documentation about each request's purpose
- Share authentication setup instructions separately
Team standards:
- Naming conventions: Consistent set and file naming
- Documentation: Clear descriptions for each request
- Version control: Track changes to shared sets
- Security: Avoid sharing sensitive authentication data
Onboarding New Team Members
Create "starter sets" that include:
- Common service endpoints: Frequently used APIs
- Example requests: Well-documented example calls
- Testing patterns: Standard testing workflows
- Environment configurations: Different deployment targets
Quality Assurance
Regression Testing
Build sets for:
- Smoke tests: Basic functionality verification
- Full regression: Comprehensive testing suites
- Performance baselines: Standard performance test configurations
- Edge cases: Boundary condition and error testing
Release Testing
Create release-specific sets:
- Pre-release validation: Test new features
- Compatibility testing: Verify backward compatibility
- Integration testing: Multi-service interaction tests
- User acceptance: End-user scenario testing
Advanced Set Management
Set Organization Strategies
By Environment
Production-Services/
├── production-wms.json
├── production-wfs.json
└── production-arcgis.json
Development-Services/
├── dev-wms.json
├── dev-wfs.json
└── dev-arcgis.json
By Project
Project-Alpha/
├── alpha-mapping-services.json
├── alpha-data-apis.json
└── alpha-integration-tests.json
Project-Beta/
├── beta-geospatial-services.json
└── beta-analysis-apis.json
By Service Type
WMS-Collections/
├── weather-wms.json
├── cadastral-wms.json
└── satellite-wms.json
API-Collections/
├── authentication-apis.json
├── data-management-apis.json
└── reporting-apis.json
File Management Best Practices
Naming Conventions
- Descriptive names:
company-production-wms-2024.json - Version information: Include dates or version numbers
- Environment indicators: dev, staging, prod prefixes
- Service type: wms, wfs, rest, arcgis suffixes
Storage Organization
- Dedicated folder: Create a folder specifically for Quetzly sets
- Backup strategy: Regular backups of important configurations
- Version control: Track changes to critical sets
- Documentation: Maintain README files explaining set purposes
Data Security and Privacy
Sensitive Information Handling
What to avoid in sets:
- ❌ Passwords: Never save passwords in clear text
- ❌ API keys: Avoid saving sensitive API keys
- ❌ Tokens: Don't save short-lived authentication tokens
- ❌ Personal data: Avoid test data with personal information
Best practices:
- ✅ Use placeholders: Replace sensitive values with
[YOUR-API-KEY] - ✅ Document separately: Keep authentication info in secure documentation
- ✅ Environment variables: Reference environment-specific configs
- ✅ Team guidance: Provide setup instructions without exposing secrets
Sharing Safely
- Review before sharing: Check for sensitive information
- Use placeholders: Replace secrets with descriptive placeholders
- Provide setup docs: Include separate setup instructions
- Version control: Use private repositories for team sets
Troubleshooting Sets
Common Import Issues
File format errors:
- Check file extension: Must be
.json - Validate JSON: Use a JSON validator if import fails
- Check encoding: Ensure UTF-8 encoding
- File corruption: Try re-exporting the original set
Missing configurations:
- Incomplete exports: Ensure all necessary data was saved
- Version compatibility: Verify set was created with compatible Quetzly version
- Custom settings: Some advanced settings may not transfer
Authentication issues:
- Missing credentials: Authentication info may need manual entry
- Token expiration: Refresh any time-sensitive authentication
- Environment differences: Adjust URLs for different environments
Performance Considerations
Large sets:
- Loading time: Very large sets may take time to import
- Memory usage: Many requests can impact application performance
- Organization: Break large sets into smaller, focused collections
Optimization tips:
- Remove unused requests: Clean up sets regularly
- Focus sets: Create purpose-specific rather than catch-all sets
- Regular maintenance: Update and prune sets periodically
Integration with Other Features
Sets and History
- History to Sets: Save frequently used requests from history
- Sets validation: Use history to verify set configurations work
- Pattern recognition: Identify useful patterns for set creation
Sets and Monitoring
- Monitor from Sets: Create monitoring configurations from proven sets
- Validation sets: Use sets to verify monitoring endpoint configurations
- Backup monitoring: Save monitoring configs as sets
Sets and API Testing
- Quick setup: Load sets to rapidly configure testing scenarios
- Baseline testing: Use sets as starting points for new tests
- Consistency: Ensure consistent testing across team members
What's Next?
Now that you understand Sets management:
- Learn about Monitoring to continuously track your critical endpoints
- Return to Send Requests to apply your saved configurations
- Review History to identify requests worth saving as sets
Ready to monitor your APIs? Continue to Monitor to learn about continuous endpoint monitoring and alerting.